Signs You May Be Experiencing Overwhelming Stress and How to Manage It | Safe and Sound
Stress is a natural response of the body to cope with the pressures of work, life and social relationships. However, when stress becomes severe and prolonged, it can have negative effects on physical and mental health. Recognizing the signs early and finding effective ways to deal with it will help you control stress better, preventing serious consequences.
Phi Thuy Linh | Bachelor of Public Health – Mental Health Care Application Safe and Sound
Institute of Medical Technology Applications
1. Signs of excessive stress
According to psychologists, excessive stress can manifest in many different ways, affecting a person's physical, mental and behavioral health. Recognizing these signs early will help you proactively adjust your life and avoid negative consequences. Below are some common signs when stress becomes serious.
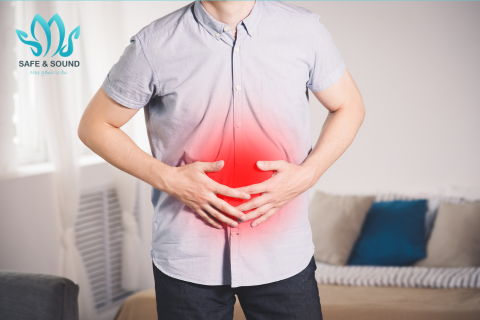
Too much stress can cause digestive problems.
1.1. Physical signs
Stress not only affects the mind but also causes negative reactions to the body. Some easily recognizable signs are:
- Chronic fatigue : Even though not overworked, the body still feels lethargic and lacks energy.
- Sleep disorders : Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep or waking up many times during the night are some of the common symptoms.
- Headache, dizziness : Prolonged stress can cause tension headaches, migraines or dizziness.
- Rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath : This is a symptom when the nervous system is overstimulated due to stress.
- Digestive problems : Stomach pain, nausea, diarrhea or constipation may occur when you are under severe stress.
- Muscle tension, body aches : When stressed, the body tends to stiffen muscles, especially in the shoulders, neck and back.
- Weakened immune system : Chronic stress makes the body more susceptible to illnesses, from colds to other inflammatory problems.
1.2. Psychological and emotional signs
Stress has a strong impact on psychology, causing negative emotions such as:
- Anxiety, insecurity : You always feel nervous, think negatively and fear bad things happening.
- Irritability, impatience : Small things can make you angry and overreact to people around you.
- Loss of motivation, loss of interest : When you're stressed out, you may no longer feel interested in work, hobbies, or recreational activities you once enjoyed.
- Difficulty concentrating, memory loss : Prolonged stress can affect thinking ability, reduce work and study performance.
- Mood swings : Some people may experience feelings of depression and sadness, while others may become more sensitive and vulnerable.
- Feelings of helplessness and despair : When stress persists without being resolved, you may fall into a state of despair, losing faith in yourself and life.
- Increased negative thinking : You may frequently blame yourself, feel like you're not good enough, or worry about things that haven't happened yet.
- Prone to obsessive or overthinking : You may think about a problem over and over again without being able to find a solution, which increases the severity of the stress.
1.3. Behavioral signs

Substance abuse may be a sign that you are under too much stress.
Psychologists share that, in addition to physical and psychological, stress also changes your behavior such as:
- Avoiding communication : You tend to want to be alone, not wanting to interact with friends, family or colleagues.
- Overworking or procrastinating : Some people may throw themselves into work to forget stress, while others procrastinate because they can't concentrate.
- Substance abuse : Using more alcohol, beer, coffee or cigarettes to relieve stress, however this is only a temporary solution and can be harmful to your health in the long run.
- Eating disorders : Some people overeat when stressed, while others skip meals, leading to malnutrition or uncontrolled weight gain.
- Self-destructive behavior : Some severe cases can lead to self-harm such as hair pulling, skin picking or even negative thinking.
- Lack of patience at work and in life : When you are under too much stress, you easily feel out of control and get angry with colleagues, family and friends.
- Easily give up on personal goals : When you are too stressed, you can lose motivation to pursue important plans and goals in life.
2. How to deal with excessive stress
2.1. Adjust to a scientific lifestyle
Psychologists recommend lifestyle changes that can help reduce stress, such as:
- Get enough sleep : Make sure to sleep 7-8 hours a day to restore your body and mind.
- Eat healthy : Add foods rich in vitamins and minerals such as green vegetables, fruits, salmon, walnuts to reduce stress.
- Exercise regularly : Walking, yoga, meditation, swimming or cycling will help relax both physically and mentally.
- Reduce exposure to electronic devices : Limit time spent on phones, computers, and social media to avoid information overload.
- Get involved in social activities : Connecting with the community, volunteering or joining a club you enjoy helps reduce stress and create positive motivation.
- Find joy in the little things : Spend time reading, listening to music, painting or taking care of plants to relax your mind.
2.2. Psychological and emotional management techniques
- Practice deep breathing : Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, then exhale slowly to help calm your nervous system. You can practice the 4-7-8 or 4-4-4 breathing method.
- Journaling : Record your feelings and thoughts to learn about what's causing your stress and help you better control your mood.
- Talk with relatives and friends : Sharing your feelings and thoughts helps you relieve stress and receive encouragement from people around you.
- Meditation and mindfulness : Helps you focus on the present, reducing anxiety about the past or future.
- Learn to say "no" : Setting limits for yourself and saying no to unnecessary things helps you reduce stress.
2.3. Seek the help of a psychologist
If the above measures do not help to improve your stress, you should seek advice and support from a mental health professional. Some useful therapies include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) : Helps change the way you think and react to stress.
- Relaxation therapy : Combines meditation, massage, and stress-reduction techniques.
- Talk therapy : Helps you better understand what causes stress and how to deal with it.
.png)
2.4. Create a positive living and working environment
- Arrange the space neatly : A clean, airy environment helps improve psychology better.
- Plan your work properly : Allocate work and rest time to avoid overload.
- Take time for yourself : Participate in favorite activities such as reading, listening to music, traveling to relax.
Recognizing and dealing with stress properly will help you maintain good mental health and improve your quality of life. If you feel that excessive stress is seriously affecting your psychology, do not hesitate to seek timely support from a psychologist.
Safe and Sound Clinic - Family health and psychological support
With a team of experienced doctors and specialists, Safe and Sound Clinic is a pioneer in comprehensive health care with health care services from medicine to psychology.
“Early prevention - Timely support - Long-term companionship”.
If you have any doubts or experience any physical or mental health problems, please contact HOTLINE 0964 778 911 (Phone/Zalo, 24/7) for answers and support as soon as possible!
HOW TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT for online or in-person consultation with an expert
- At SnS Clinic - IMT Institute
- Or download and schedule a consultation on the Safe and Sound app to manage and track your schedule anytime, anywhere.
Safe and Sound (SnS) - Institute of Applied Medical Technology (IMT)
See also:
How to effectively reduce nervous tension: Sharing from a psychological expert
A Beginner's Guide to Practicing Mindfulness to Reduce Stress




